CADMIUM AND CADMIUM COMPOUNDS FACT SHEET
Updated in May 2021
This fact sheet is part of a series of chemical fact sheets developed by TURI to help Massachusetts companies, community organizations and residents understand a chemical’s use and health and environmental effects, as well as the availability of safer alternatives. It was updated in May 2021.
Cadmium (Cd) is a soft, silver-white, low-melting-point metal. Cadmium is extracted mainly as a byproduct of the mining and processing of zinc, lead or copper. Cadmium has many uses in industry and consumer products, mainly in batteries, pigments, coatings and plating solutions, polymer stabilizers, metal alloys and semiconductors for solar cells.
Due to its serious adverse effects on human health and the environment, cadmium is subject to multiple regulations at the state, federal, and international levels. In 2018, Massachusetts facilities subject to TURA reported the use of over 160,000 pounds of cadmium and cadmium compounds.
Cadmium and cadmium compounds were designated as higher hazard substances under the Toxics Use Reduction Act (TURA) in January 2008, which reduces the associated reporting thresholds to 1,000 pounds per year.
Learn more about health and environmental impacts, uses and releases, alternatives and regulatory context.
Cadmium Facts, Updated May 2021
-
Health and Environment
Updated May 2021
Cadmium: Health and Environmental Impacts
Please note: Toxicity data is constantly evolving and as such the data presented here are valid as of May, 2021. Updated TURA data is available at www.turadata.org.
Human health and environmental impacts may result when exposure to cadmium and cadmium compounds occurs. The following is a summary of potential exposure routes and the associated human health and environmental impacts.
Exposure Routes
For the general population, the major route of exposure to cadmium is ingestion of food. Smoking is another major source of cadmium intake. Ingestion of drinking water and inhalation of cadmium aerosols from the atmosphere are also potential sources of cadmium exposure.1 The primary route of occupational exposure is inhalation of dust and fumes. Accidental ingestion of dust from contaminated hands, cigarettes, or food can also occur. Occupational exposure occurs primarily in smelting and refining zinc, lead, and copper ores; welding or remelting of cadmium-coated steel; working with solders that contain cadmium; producing, processing, and handling cadmium powders; spraying cadmium containing pigments; and processing scrap metal containing cadmium.2
Human Health Effects
Acute (Short-term) Health Effects
CADMIUM FACTS
Chemical Formula Cd CAS Number 7440-43-9 Vapor Pressure 1 mm Hg at 394oC; negligible @ 20oC Boiling Point 765oC Reactivity Cadmium dust may ignite upon contact with air. [Danger Pyrophoric liquids; Pyrophoric solids].2,3 Water Solubility Cadmium is insoluble; Cadmium compounds solubility varies from insoluble to soluble.1,4 Description Soft, silver-white metal4 - Cadmium is irritating to the nose and throat.
- Inhalation of very high levels of Cd can severely damage the lungs and may cause death.1
- Ingestion of very high levels of Cd severely irritates the stomach, leading to vomiting, diarrhea, and sometimes death.5
Chronic (Long-Term) Health Effects
- Cadmium is carcinogenic to humans. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies cadmium and cadmium compounds as Group 1 carcinogens (carcinogenic to humans), causing lung cancer and with positive associations for kidney and pancreatic cancer.3,6,7 The U.S. EPA classifies cadmium as a Group B1 (probable human) carcinogen by inhalation.8 NIOSH considers cadmium (and cadmium compounds) dust and fumes to be potential occupational carcinogens.5,9
- Recent studies link exposure to Cd to bladder cancer and chronic obstructive airway disease (COPD).10
- Breathing airborne particles containing Cd over long periods of time may cause lung damage and fragile bones.11
- Kidney damage can occur from accidental ingestion or inhalation from cadmium dust.12
- Cadmium is a potential reproductive and developmental toxicant. California has designated cadmium causing male reproductive toxicity under its Proposition 65 regulation.13
- Animal studies indicate that eating or drinking cadmium may cause high blood pressure, iron-poor blood, liver disease, osteoporosis, nerve, or brain damage.1
Environmental Hazards
Cadmium enters the environment primarily through human activities such as mining and smelting operations, fuel combustion, disposal of metal-containing products, and application of phosphate fertilizer or sewage sludges. Cadmium that is in or attached to small particles can enter the air, especially during incineration. The main species of cadmium found in the atmosphere is cadmium oxide, though some cadmium salts, such as cadmium chloride, also exist. In water, cadmium can exist as the hydrated ion, or as ionic complexes with other inorganic or organic substances.14
Cadmium in its ionic form is toxic to a variety of plants, animals, and human cells. When cadmium is exposed to soil and aquatic life, plants and animals can absorb the chemical, causing growth development issues.1 A tragic mass cadmium poisoning case in Toyama Prefecture, Japan in 1950 showed cadmium’s toxicity. The cadmium had leached from wastes at a nearby lead-zinc mine and contaminated the village water supply and caused itai-itai disease in people exposed to the contamination.15,16 Symptoms of this disease include kidney dysfunctions and softening of the bones.17,18,19
-
Use Nationally and in Massachusetts
Updated May 2021
Cadmium: Use Nationally and in Massachusetts
Use in the United States
In the U.S the major use of cadmium compounds is cadmium hydroxide used in the manufacture of nickel-cadmium batteries.20 Other uses include manufacture of pigments (as cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide), coatings and plating solutions (as cadmium fluoroborate, cadmium iodide, cadmium oxide, and cadmium sulfate), and stabilizers for plastics (as cadmium oxide, cadmium laurate, and cadmium stearate).
Batteries: Nickel cadmium is currently the most widely used cadmium battery, and accounts for nearly all of the cadmium used in batteries. This amounts to the majority of the total cadmium used in the United States. Silver cadmium is also used in batteries for aircraft and space applications.
Pigments: Cadmium pigments account for a small percentage of the cadmium used in the United States. Most cadmium pigments are used in plastics applications. Other uses of cadmium pigments include paints, ceramic ware, glass, and decorative coatings for metals, printing inks, and rubber.
Coatings and Plating Solutions: Cadmium coatings are applied to steel products such as aircraft landing gear components, automotive brake parts, fasteners of all types, and springs. In addition, cadmium coatings have been widely used on electrical and electronic components, such as connectors, equipment housings, and switches. Cadmium usage for coatings and plating solutions in the U.S. has been greatly reduced since the 1960s, and especially in the 1990s, due to restrictions placed on industries by the U.S. EPA for their use of cadmium.20
Between 1991 and 2020, total U.S. Cadmium Import and Exports have declined from 2488 to 193 metric tons. Although this is a 92% reduction in Imports and Exports from the U.S., domestic production and consumption of cadmium have been withheld, since 2011.21
New uses for cadmium in the synthesis of ultrathin photovoltaic films comprised of cadmium Selenide (CdSe) and cadmium Telluride (CdTe) nanocrystals are emerging uses.22,23
Use in Massachusetts
Between 1990 and 2018 Massachusetts companies that are required to report toxic chemical usage under TURA (referred to as “TURA filers”) reported an 81% reduction in the overall use of cadmium and cadmium compounds, even after lowered Higher Hazard Substance (HHS) thresholds brought in new filers beginning in 2008.
Table 1 summarizes the use of cadmium and cadmium compounds in Massachusetts by industry sector, based on toxics use reduction reporting data from Massachusetts companies.
Table 1: Massachusetts Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds Consumption by Industry Sector (1990-2018)
Industry Sector Facility Name Location 1990 (Use Pounds) 2018 (Use Pounds) Custom Compound Resins AlphaGary Leominster 433,952 0 Clariant Corp Master Batches Division Holden 46,300 0 Dampney Company Everett 0 1,939 American Insulated Wire Corp Attleboro 180,000 0 Plastics Film and Sheet Regalite Plastics Corporation Newton 37,368 0 Vernon Plastics Company Haverhill 34,921 0 Wire and Electronic Devices Checon Corporation Attleboro 0 124,000 Polymetallurgical Company North Attleboro 0 2,369 Umicore Electrical Materials Attleboro 0 7,237 Metal Products Manufacturing BASF Catalysts LLC Plainville 69,800 0 Brainin Advance Industries Attleboro 0 2,351 Metalor Technologies USA Attleboro 18,180 0 Engineered Materials Solutions Inc. Attleboro 0 0 Plating/Electroplating Central Metal Finishing North Andover 0 884c New Method Plating Corp Worcester 22,360 14,600 Purecoat North LLC Belmont 0 150c Texas Instruments Attleboro 16,000 0 Valley Plating Springfield 0 4,528 Westfield Electroplating Westfield 0 1,027 Electronic Recyclers Electronic Recyclers International Holliston 0 3,135 Total Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds Use 858,881 162,220 aBlank cells indicate that cadmium and cadmium compounds were not reported under by that company for the corresponding year. Note that the HHS reporting threshold for 2018 is 1,000 pounds.
bUse categories were assigned based on TURI’s interpretation of facility-reported information under TURA.
cReported below the 1,000 pound threshold
Source: Massachusetts Toxics Use Reduction Act data, 2019.For the purpose of assessing trends, industry sectors were aggregated into six use categories: Custom Compound Resins, Plastics Film and Sheet, Wire and Electronic Devices, Metal Products Manufacturing, Plating and Electroplating, and Electronics Recycling.
Plastics and Resins Manufacture
Uses of cadmium and cadmium compounds in the plastics and resins sectors are associated with stabilizer additives and pigments in plastic and synthetic products.16 Plastics formulators in Massachusetts, including manufacturers of custom resin formulations, and manufacturers of plastic products such as sheet and film plastic, had eliminated their reportable uses of cadmium by 2003. A new manufacturer of protective resins began reporting in 2008 due to lowered higher hazard substances (HHS) reporting thresholds.
Suitable substitute additives and pigments were identified and used by this industry within 4 years of initial reporting. AlphaGary continued to manufacture custom polymer compounds containing cadmium until 2002. However, it reduced its use of cadmium by over 90% within the first year of reporting.
Wire and Wiring Device Manufacture
American Insulated Wire Corp used plastics containing cadmium compounds in 1990 only. This company, which manufactures electrical and electronic wire, cable and cord set products, serving a variety of markets, continued to manufacture products, but was able to reduce its use of cadmium compounds below the reporting threshold within one year of reporting.
Checon Corporation began reporting cadmium compounds in 2004. Checon supplies electrical contact materials for a variety of applications, including industrial control, electrical switch, wiring device, appliance, and automotive. Two new tape, wire, and button manufacturers began reporting after 2008 due to lowered HHS reporting thresholds.
Metal Products Manufacturing
Cadmium is used in low melting point and brazing alloys with bismuth, lead and tin. Cadmium containing alloys are used as bearings, solders and copper hardeners in fire detection devices, high-speed machinery, automotive components, and nuclear reactor control rods 1,24 Alloy manufacturing industries in Massachusetts include nonferrous rolling and drawing, primary metal products, and motor vehicle parts and accessories. Products manufactured by companies in Massachusetts within these industry sectors include:
- Silver powder and cadmium oxide bars
- Silver cadmium alloy forming and casting
One new company, making precision metal parts, began reporting in 2008 due to the reporting thresholds.
Plating and Electroplating
Production processes conducted in the electroplating sector include cadmium electroplating and cadmium cyanide electroplating.
Between 1990 and 2018, cadmium use in electroplating applications decreased by 45% in Massachusetts. This decrease was due primarily to the elimination of cadmium-cyanide electroplating operations at the Texas Instruments facility in Attleboro in 2000. Some plating shops have had success with their supply chains and customers in eliminating cadmium. Four new plating and electroplating filers began reporting after 2008 due to lowered HHS reporting thresholds.
Companies Entering the Reporting Universe
The TURA Administrative Council designated cadmium and cadmium compounds as higher hazard substances under TURA in January 2008, which reduces the reporting threshold for to 1,000 pounds per year. As a result, 10 new TURA filers reported due to the lower reporting threshold and currently there are still 10 filers that are reporting due to the lower threshold (though two of those reported amounts below reporting thresholds).
Inputs and Outputs in Massachusetts
Overall, Massachusetts has experienced an 81% reduction in the use of Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds since 1990.
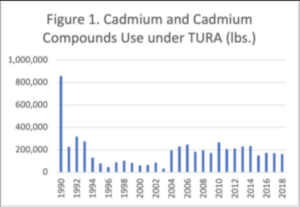
Figure 1 shows the use of cadmium and cadmium compounds reported under TURA from 1990 to 2018. There has been an 81% reduction in use of cadmium and cadmium compounds, since 1990, even with the addition of new filers under the HHS reporting threshold. Significant reductions in the use of cadmium stabilizers in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) occurred in the second year of reporting by AlphaGary and American Insulated Wire.
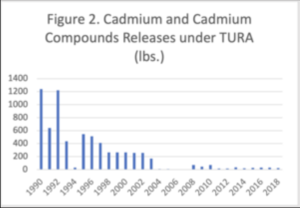
Figure 2 shows the releases of cadmium and cadmium compounds reported under TURA from 1990 to 2018. Releases have reduced by 98% overall, but have increased from their lowest point, before HHS thresholds came into effect.
-
Alternatives
Updated May 2021
Cadmium: Alternatives
Due to the hazards associated with cadmium and cadmium compounds, facilities should seek out opportunities to reduce their use wherever possible. Opportunities include adopting safer alternatives for specific functions or applications and minimizing use through improved efficiencies if alternatives are not available.
With an increase in stringent global restrictions, many companies have redesigned their products and processes to use safer alternatives. The significant reduction in use of cadmium and cadmium compounds by TURA filers indicates that toxics use reduction options are available for many applications and that Massachusetts companies are taking advantage of those opportunities. Where input substitution is not yet feasible, many facilities report improved operations and maintenance and production unit redesign in order to use cadmium as efficiently as possible. Examples of this are weirs to reduce drag out from plating baths, retooling to reduce burrs on parts, and automatic feeds to reduce waste and operator exposure.
Substantial information is available on cadmium alternatives for soldering, plating, stabilizers, and pigments used in plastics. We also provide information on emerging alternatives to cadmium-bearing batteries.
Alternatives for Plastics and Pigments Sector
Pigments in Plastic Products
Cadmium is used to create a range of yellow colors in plastics formulations.25 Cadmium sulfides and sulfo-selenides are used in pigments to create a family of yellow, orange and red pigments. Cadmium yellow is created using cadmium sulfide (CdS), cadmium red is cadmium selenide (CdSe) and cadmium orange is an intermediate cadmium sulfoselenide.25,26 Cadmium yellow is sometimes mixed with a hydrated chromium oxide pigment to create a bright, pale green mixture called cadmium green.27,28,29 Cadmium has also been used as a weathering, light and heat stabilizer in certain plastic formulations, especially in PVC.
Processes used in Massachusetts for cadmium use as pigments and stabilizer additives include:
- Polymer compounding
- Plastic extrusion on copper wire
- Plastics blending and extruding
- Flexible plastics calendaring
A variety of alternatives are available for cadmium in yellow pigments. Some alternatives pose significant health and environmental hazards, while others are superior from a health and environmental perspective. As early as the beginning of the 1990s, many firms found that they were able to replace cadmium in the majority of pigments in which it had been previously used. Alternatives include inorganic pigments based on acid solutions of synthetic oxo-nitrides, iron oxide pigments, bismuth vanadate pigments, organic and inorganic pigment blends using titanium dioxide, mixed metal oxide titanites, and/or iron oxide, rutile tin zinc compounds and others.
Stabilizers
Cadmium has been used as a weathering, light and heat stabilizer primarily in PVC plastic formulations. In the United States, use of cadmium-bearing stabilizers has decreased since 1990. Alternatives for cadmium stabilizers include barium-zinc, calcium-zinc, antimony, organotin, and organic compound stabilizers.24 While these alternatives meet the necessary performance criteria for specific applications, antimony and organotin stabilizers are not considered to be safer substitutes because of their respective high toxicities.
Alternatives for Coating and Plating Uses
Cadmium coatings are applied to various base metals to impart excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine and alkaline environments. In addition to corrosion protection, cadmium coatings provide a low coefficient of friction and therefore good lubricity, good electrical conductivity, easy solderability, and reduced risks of operating mechanisms being jammed by corrosion debris for many components in a wide range of engineering applications throughout industry.
Methods to reduce the use of cadmium in metal plating applications include:
- Product redesign to eliminate the need for the coating.
- Use a metal deposition technology that does not require a plating bath (e.g. vapor-deposited aluminum).
- If these alternatives are not viable due to required surface characteristics or cost, various organic polymers, tin alloys, zinc, and binary alloys of zinc with cobalt, iron, manganese, nickel, and silicon offer alternatives to cadmium for a variety of applications, including:
- Metallic-ceramic coatings have successfully replaced cadmium in more expensive military applications, including landing gear axles of modern aircraft, gas-turbine-engine compressor sections, and allied parts.
- An improved method for the deposition of corrosion-resistant aluminum coatings for aerospace applications was developed. This method used ion- vapor-deposited (IVD) aluminum (a series of aluminum alloys) as an alternative.30,31
- Aluminum-molybdenum coatings have been investigated as a possible alternative to cadmium in applications with specialized requirements, such as aerospace applications.30,31
The ability to replace a cadmium coating with a zinc-based alloy depends on the specific characteristics required. Metallic-ceramic coatings, using zinc, aluminum, or alloys of these metals, possess the corrosion resistance characteristic of cadmium without the same environmental issues, although often at a higher cost. Replacing cadmium for plating of fasteners in military and aerospace applications may pose difficulties due to the unique requirements of those applications, although the military is evaluating alternatives to cadmium.
Alternatives for Batteries
Because it represents the biggest overall use of cadmium nationwide, it is appropriate to touch upon the availability of alternatives to nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries.
Currently, the principal alternatives to NiCd batteries are lead-acid, nickel-metal hydride, and lithium-ion batteries as well as fuel cells.32 Ni-metal hydride batteries possess substantially greater energy-storage capacity and power per unit weight or volume than lead-acid batteries but are very expensive.33,34 Since 1991, rechargeable Ni-metal hydride batteries, with low discharge rates and long cycling stability, have been used for consumer applications such as portable computers, cordless appliances and communication equipment.32 A power-optimized version of Ni-metal hydride batteries are now fitted to commercialized hybrid vehicles.34 Lithium-ion and sodium–nickel chloride batteries have a lower environmental impact than lead–acid, nickel–cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries.35
-
Regulatory Context
Updated May 2021
Cadmium: Regulatory Context
Due to their serious adverse effects on human health, cadmium and its compounds are subject to multiple regulations at the state, federal, and international levels. Cadmium and cadmium compounds are regulated as carcinogens, and cadmium is regulated as a male developmental toxicant, under California’s Safe Drinking Water and Toxics Enforcement Act of 1986 (Proposition 65).14
EPCRA: Reportable under TRI36, Subject to Tier II reporting requirements.
CAA: Hazardous air pollutant.1
RCRA: Cadmium is a hazardous waste under RCRA under several circumstances.1
Occupational exposures: The OSHA permissible exposure limit (PEL) for airborne exposure to Cd for an eight-hour work shift is 5 μg/m.3,37 OSHA includes Cd on its list of known human carcinogens.
SDWA: The maximum contaminant limit set for drinking water is 0.005 mg/L.38
FDA: Limits the amount of Cd in food colors to 15 parts per million (ppm).1International
The Dangerous Substances Directive (76/769/EEC) prohibits the use of cadmium and its compounds in finished plastic products, in paints, as a stabilizer in PVC products (except where required for safety reasons), and for plating metallic products or components in a variety of sectors. In addition, those cadmium compounds that are listed as carcinogens are restricted for use in “substances and preparations placed on the market for sale to the general public.”39
As part of its REACH regulation, the European Union (EU) restricts the placement of finished articles colored with cadmium if their cadmium content (expressed as cadmium metal) exceeds 0.01 % by mass of the plastic material.8 This restriction does not affect products when the use of cadmium pigments relates to a safety issue.
Cadmium is one of the six chemicals regulated under the Restriction on Hazardous Substances (RoHS), which applies to electrical and electronic equipment sold in the EU.40 Under RoHS, the maximum allowable concentration of cadmium by weight in a homogeneous material is 0.01%. -
References
Updated May 2021
Cadmium: References
1 US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC. (1999). Toxicological Profile for Cadmium . Atlanta.https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp5-c6.pdf
2 U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2021). Cadmium. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database.https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cadmium
3 World Health Organization. (2010). PREVENTING DISEASE THROUGH HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS:EXPOSURE TO CADMIUM: A MAJOR PUBLIC HEALTH CONCERN . Switzerland. https://www.who.int/ipcs/features/cadmium.pdf
4 International Labor Organization. (2005, April). International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs). ICSC database: International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs).
5 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2010, November 19). NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards 3rd Printing. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2005-149/default.html.
6 World Health Organization, IARC . (2011). Monograph: Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds. Switzerland.https://monographs.iarc.who.int/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100C-8.pdf
7 Bertin, G., & Averbeck, D. (2006). Cadmium: cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences (a review). Biochimie, 88(11), 1549.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.10.001
8 European Union. (2020, November 9). ECHA Substance Infocard: Cadmium. European Chemicals Agency.https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.028.320?_disssubsinfo_WAR_di.
9 Kellen, E., Zeegers, M. P., Hond, E. D., & Buntinx, F. (2007). Blood cadmium may be associated with bladder carcinogenesis: The Belgian case–control study on bladder cancer. Cancer Detection & Prevention, 31(1), 77–82.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.cdp.2006.12.001
10 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014, December 4). CDC – Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH): Cadmium compounds (as Cd) – NIOSH Publications and Products. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7440439.html.
11 Zheng, L., Jiang, Y.-L., Fei, J., Cao, P., Zhang, C., Xie, G.-F., Wang, L.-X., Cao, W., Fu, L., & Zhao, H. (2021). Circulatory cadmium positively correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 215.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112164
12 Oh, C. M., Oh, I. H., Lee, J. K., Park, Y. H., Choe, B. K., Yoon, T. Y., & Choi, J. M. (2014). Blood cadmium levels are associated with a decline in lung function in males. Environmental research, 132, 119–125.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.04.008
13 California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment. (2021, March). Proposition 65 No Significant Risk Levels (NSRLs) for Carcinogens and Maximum Allowable Dose Levels (MADLs) for Chemicals Causing Reproductive Toxicity. oehha.ca.gov.https://oehha.ca.gov/proposition-65/general-info/current-proposition-65-no-significant-risk-levels-nsrls-maximum.
14 Prozialeck, W. C., & Edwards, J. R. (2012). Mechanisms of cadmium-induced proximal tubule injury: new insights with implications for biomonitoring and therapeutic interventions. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics, 343(1), 2–12.https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.110.166769
15 Midwest Research Institute . (1993, September). EPA: Locating and Estimating Sources of Cadmium. Cary,North Carolina.https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2020-11/documents/cadmium.pdf
16 Wikimedia Foundation. (2021, February 26). Itai-itai disease. Wikipedia
17 Nishijo, M., Nakagawa, H., Suwazono, Y., Nogawa, K., & Kido, T. (2017). Causes of death in patients with Itai-itai disease suffering from severe chronic cadmium poisoning: a nested case-control analysis of a follow-up study in Japan. BMJ open, 7(7), e015694.https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015694
18 Engström, A., Michaëlsson, K., Suwazono, Y., Wolk, A., Vahter, M., & Akesson, A. (2011). Long-term cadmium exposure and the association with bone mineral density and fractures in a population-based study among women. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, 26(3), 486–495.https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.224
19 Kazantzis G. Cadmium, osteoporosis and calcium metabolism. Biometals. 2004 Oct;17(5): 493-8.doi:10.1023/b:biom.0000045727.76054.f3. PMID: 15688852.
20 Butterman, W. C., & Plachy, J. (2006). MINERAL COMMODITY PROFILES CADMIUM Open-File Report 02-238. Reston, VA; U.S. DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY.
21 National Minerals Information Center. Cadmium Statistics and Information. (2020). https://www.usgs.gov/centers/nmic/cadmium-statistics-and-information.
22 Md. Hasan Ali, Md. Mahabub Alam Moon, & Md. Ferdous Rahman. (2019). Study of ultra-thin CdTe/CdS heterostructure solar cell purveying open-circuit voltage ∼1.2 V. Materials Research Express, 6(9), 1.
23 Dhanam, M., Prabhu, R. R., & Manoj, P. K. (2008). Investigations on chemical bath deposited cadmium selenide thin films. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 107(2), 289–296.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.07.011
24 Endriss, H., & haid, M. (1996). Bismuth Vanadate Pigments – an Alternative to Lead and Cadmium-Containing Plastics Pigmentations. Kunststoffe Plast Europe.
25 WOOD, A. (2000). Cadmium-Free Inorganic Pigments. Chemical Week, 18.
26 Jansen, M., & Letschert, H. P. (2000). Inorganic yellow-red pigments without toxic metals. Nature, 404(6781), 980.
https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1038/35010082
27 Hatcher, H., Tocher, A., McKenna, M., & Lane, L. (2004, January 1). Providing unique solutions: with a new pigment chemistry. Paint & Coatings Industry, 20(1), 60.
28 Mulholland, B. M. (1994). Cadmium-Free Coloured Engineering Plastics for the Automotive Industry.
29 Chromatics to discontinue production of heavy metal-based colorants. (2006). Wire Journal International, 39(10), 14.
30 Bielawski, M. (2004). Development of unbalanced magnetron sputtered Al–Mo coatings for cadmium replacement. Surface & Coatings Technology, 179(1), 10–17.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00796-5
31 Monaghan, D. P., Teer, L. L. D. G. P. A. K. C., & Bates, A. R. I. R. D. (1993). An improved method for the deposition of corrosion-resistant aluminium coatings for aerospace applications. Surface & Coatings Technology, 60(1), 592–596.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/0257-8972(93)90159-L
32 00/03493 Appropriate battery technology for a new, rechargeable, micro-solar lantern. (2000). Fuel and Energy Abstracts, 41(6), 392.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/S0140-6701(00)94565-X
33 Otto, A., & Güther, V. (1999). Development of fast kinetics metal hydride alloys and battery electrodes for high power applications.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 293, 734–736.https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(99)00347-3
34 Tirronen, T., Sukhomlinov, D., O’Brien, H., Taskinen, P., & Lundström, M. (2017). Distributions of lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride battery elements in copper converting. Journal of Cleaner Production, 168, 399–409. https://doi-org.umasslowell.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.051
35 Davis, G. A., Kincaid, L., Menke, D., Griffith, B., & Jones, S. (1994, September 1). Product side of pollution prevention: Evaluating the potential for safe substitutes. Product side of pollution prevention: Evaluating the potential for safe substitutes (Technical Report) | OSTI.GOV.https://www.osti.gov/biblio/35087.
36 Environmental Protection Agency. (2020, November 4). TRI Basis of OSHA Carcinogens. EPA.https://www.epa.gov/toxics-release-inventory-tri-program/tri-basis-osha-carcinogens.
37 Department of Labor logo UNITED STATESDEPARTMENT OF LABOR. 1910.1027 – Cadmium | Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (2020, February 18).https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.1027.
38 Environmental Protection Agency. (2021, January 5). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. EPA. https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations.
39 European Union. (2006, December 18). REACH Online. ReachOnline.https://reachonline.eu/reach/en/toc.html.
40 European Union. (2011, July 27). RoHS Directive. Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive-European Commission.https://ec.europa.eu/environment/topics/waste-and-recycling/rohs-directive_en.
