Toxics Use Reduction Act Overview
In 1989, Massachusetts passed the Toxics Use Reduction Act (TURA). This statute promotes the adoption of safer chemicals and processes in manufacturing facilities, while supporting the economic viability of Massachusetts facilities.
Whereas traditional environmental regulations focused on controlling emissions and releases of pollutants to the environment, TURA focuses on preventing the use of toxic chemicals and the generation of toxic waste. Under TURA, companies must report on their use of toxic chemicals, pay fees which support state resources for companies, and conduct TUR planning.
This course is about toxics use reduction (TUR) planning, which is a framework companies use to identify opportunities to reduce their use and generation of toxic and/or hazardous chemicals. Though TURA does not require implementation of the toxics use reduction strategies, many companies choose to do so after seeing the potential benefits.
By proactively identifying and reducing the use of harmful chemicals, businesses can improve employee health and safety, minimize environmental impact, and strengthen their environmental social governance profile. TUR planning also often leads to operational efficiencies. Through TUR planning companies can also avoid the “costs of toxics,” which includes the ever-increasing costs of disposing or mitigating hazardous waste. TUR planning also helps companies avoid potential fines and lawsuits, as well as less tangible, but no less important, impacts on customer relationships and public trust. Ultimately, adopting a TUR strategy can foster innovation, mitigate risks, and create long-term cost savings, making it a smart business practice.
TURA also created a program of technical support, resources and guidance to assist companies in Massachusetts. This includes over 1000 professionals from industry, consulting firms, government, and academia who have been trained as toxics use reduction planners. Planners work with companies in the planning process and certify that the TUR plans meet regulatory requirements and have been done in good faith. Additionally, the following agencies work together to implement and support TURA.
- The Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP): MassDEP is a regulatory agency, and is where TUR plan summaries must be submitted to by July 1 of each planning year. MassDEP also oversees TUR planner certification.
- The Office of Technical Assistance and Technology (OTA): OTA provides free and confidential technical assistance services to Massachusetts companies, including assistance with pollution prevention, toxics use reduction and resource conservation
- The Toxics Use Reduction Institute (TURI): Working in close collaboration with businesses of all sizes, as well as government agencies, local communities and international organizations, TURI helps identify actions companies and communities can take to protect workers and public health. TURI also provides training for TUR planners, companies, and the public.
- Toxics use reduction planners are professionals from industry, consulting firms, government, and academia who have been certified in toxics use reduction planning. Planners work with companies in the planning process and ensure that TUR plans meet regulatory requirements.
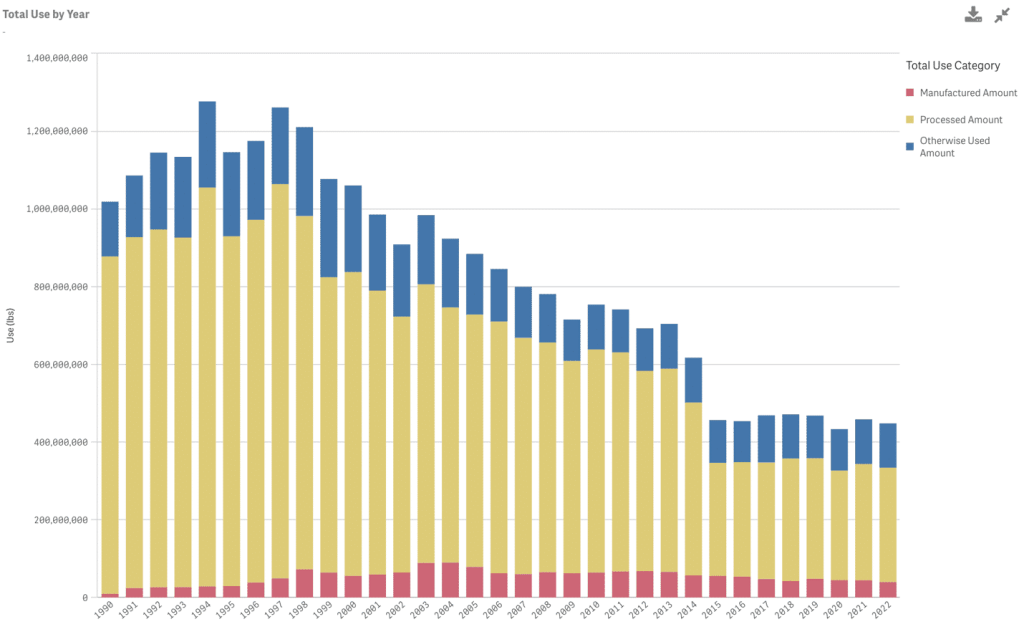
Over the past decades, Massachusetts companies have made significant progress reducing their use of toxics →
Massachusetts companies have shown incredible leadership and innovation in reducing their use of toxic chemicals and production of hazardous byproducts. The TURA model is known worldwide for its promotion of safer practices, while helping companies stay competitive. One irony of the program is that if a company reduces their toxics use enough, they will no longer be required to report or plan under TURA. The figure here, pulled from the TURA data dashboard, shows the overall decrease of total use of TURA chemicals by filers since 1990.
You can explore the TURA data dashboard for more information and charts on the use, generation and releases of TURA list toxic chemicals in Massachusetts.
